GMOS IFU overview¶
The IFU and related components are described in detail on the GMOS Web pages.
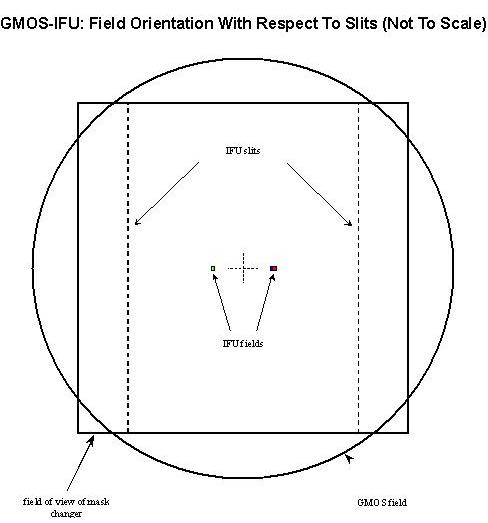
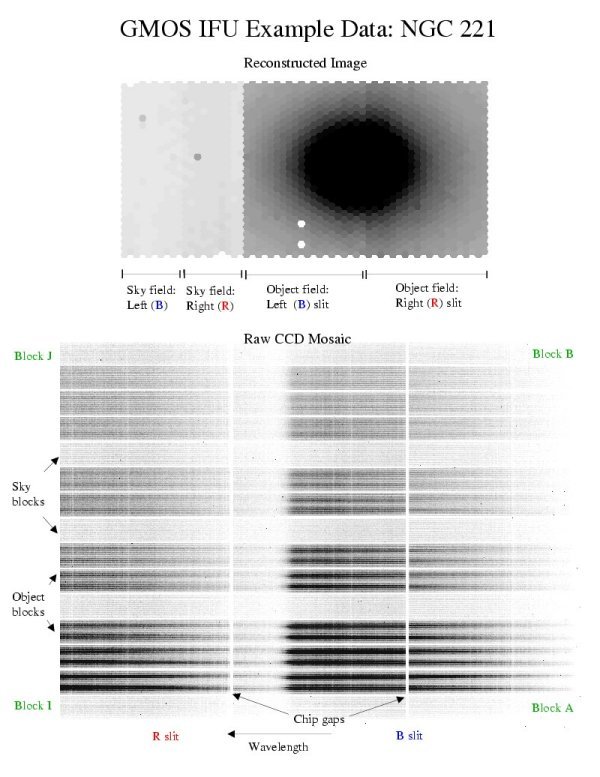
The main IFU samples a 5x7” field with a 2D array of hexagonal microlenses, coupled to 1000 optical fibres. There is also a smaller field that samples the sky background 1’ away from the target.
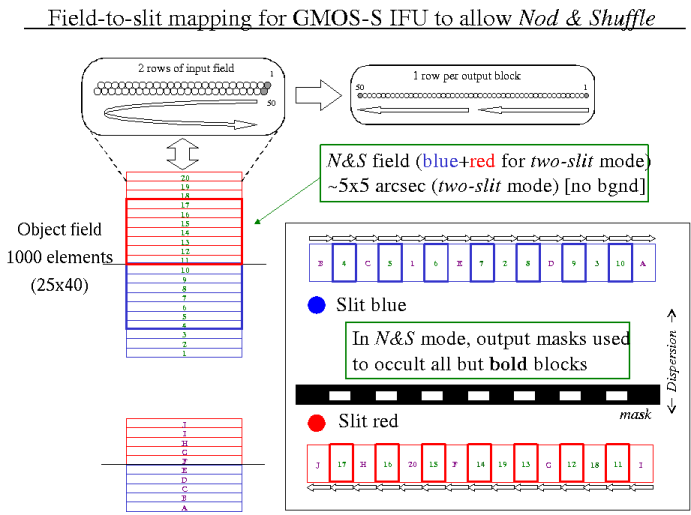
The output ends of the fibres (interleaved from both fields) are rearranged into two linear slits at the image plane of the spectrograph, which are dispersed to form two banks of spectra.
Individual fibre spectra are extracted from the detector image and used to reconstruct a 3D image of the original observation space (and thence 2D flux and velocity maps etc.).